Table of Contents
MDF Vs Plywood
So, before judging which one is stronger let’s see what MDF and Plywood are.
What is MDF?
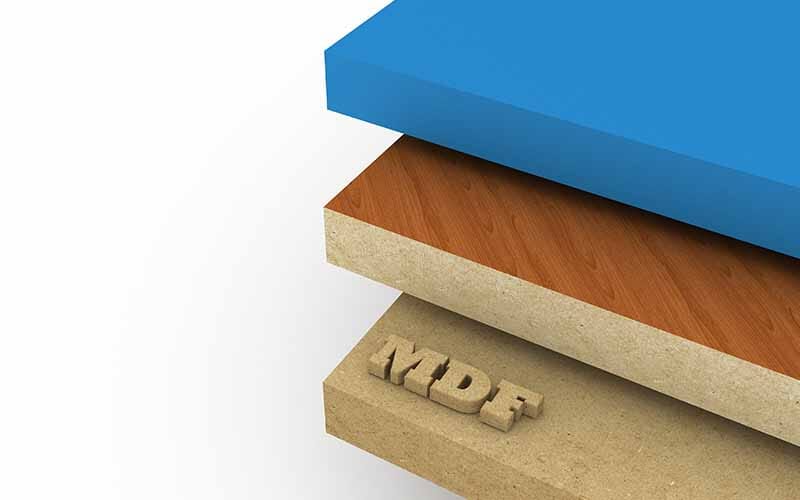
MDF is medium density fibreboard which is engineered by breaking down hardwood and softwood composites and joining them together under high pressure or high temperature with the help of an adhesive like a resin binder or wax.
What is Plywood?
Plywood is also an engineered product which is obtained by bonding several thin layers of wood veneer together into one solid piece. It is available in different grades, different thicknesses, and different sizes.
While both MDF and Plywood may appear similar, both have their strengths and weaknesses. You can decide which one to use for your project by analysing their advantages and disadvantages.
Which one is stronger?
MDF |
Plywood | |
Hardness |
MDF is not as hard as plywood. |
As it is made up of multiple layers of veneer, plywood is comparatively a hard material. |
Susceptibility to damage |
If handled roughly, it suffers damage easily. |
It is less susceptible to damage. |
Weight |
MDF is denser and weighs considerably more than plywood. |
It is comparatively light in weight. |
Sagging |
MDF is less stiff than Plywood. Placing heavy weight or applying a huge load on MDF can make it sag. |
Plywood is relatively stiff and hence it is less prone to sagging. |
Warping and shrinking |
MDF exhibits less resistance to warping and shrinking. |
Plywood has reduced warpage, shrinkage, and expansion and therefore has good dimensional stability. |
Strength |
MDF is not as strong as Plywood. |
Plywood tends to be relatively strong. |
Application |
MDF can be used for indoor use – such as in the making of decorative panels and furniture. |
Plywood can be used for making doors, floors, staircases, and outdoor furniture. |